What Causes Skin Cancer
What Causes Skin Cancer?
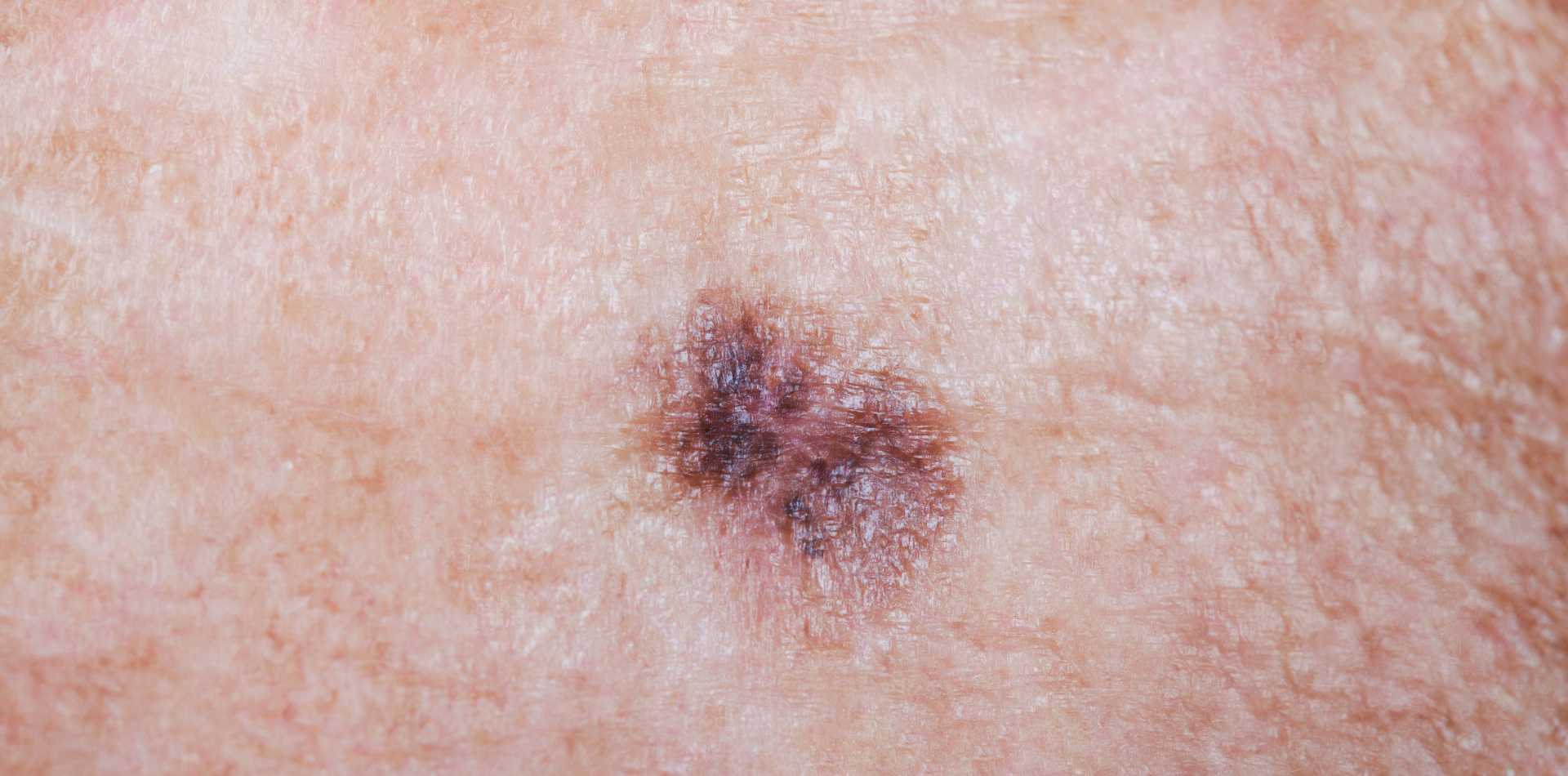
Skin cancer arises due to uncontrolled growth of abnormal skin cells, and it generally develops on skin areas that are exposed to the sun.
However, it can also form on areas of the skin not ordinarily exposed to sunlight.
There are several types of skin cancer, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma, each named after the type of skin cell from which they arise.
Causes and Risk Factors
1 - UV Radiation
Sun Exposure:
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is the primary cause of skin cancer. Both UVA and UVB rays can damage the DNA in skin cells, causing mutations.
Tanning Beds:
Artificial UV radiation from tanning beds is also a significant risk factor for developing skin cancer.
2 - Genetic Factors
Genetic Predisposition:
Some people have a genetic predisposition to develop skin cancer due to inherited genes.
Skin Type:
People with fair skin, light eyes, and light hair have a higher risk because they have less melanin, which provides some protection against UV radiation.
3 - Immunosuppression
People with weakened immune systems (e.g., due to HIV/AIDS or immunosuppressive drugs after organ transplantation) are at an elevated risk of skin cancer.
4 - Age
Although skin cancer can occur at any age, the risk increases as one gets older due to the cumulative effect of UV exposure over the years.
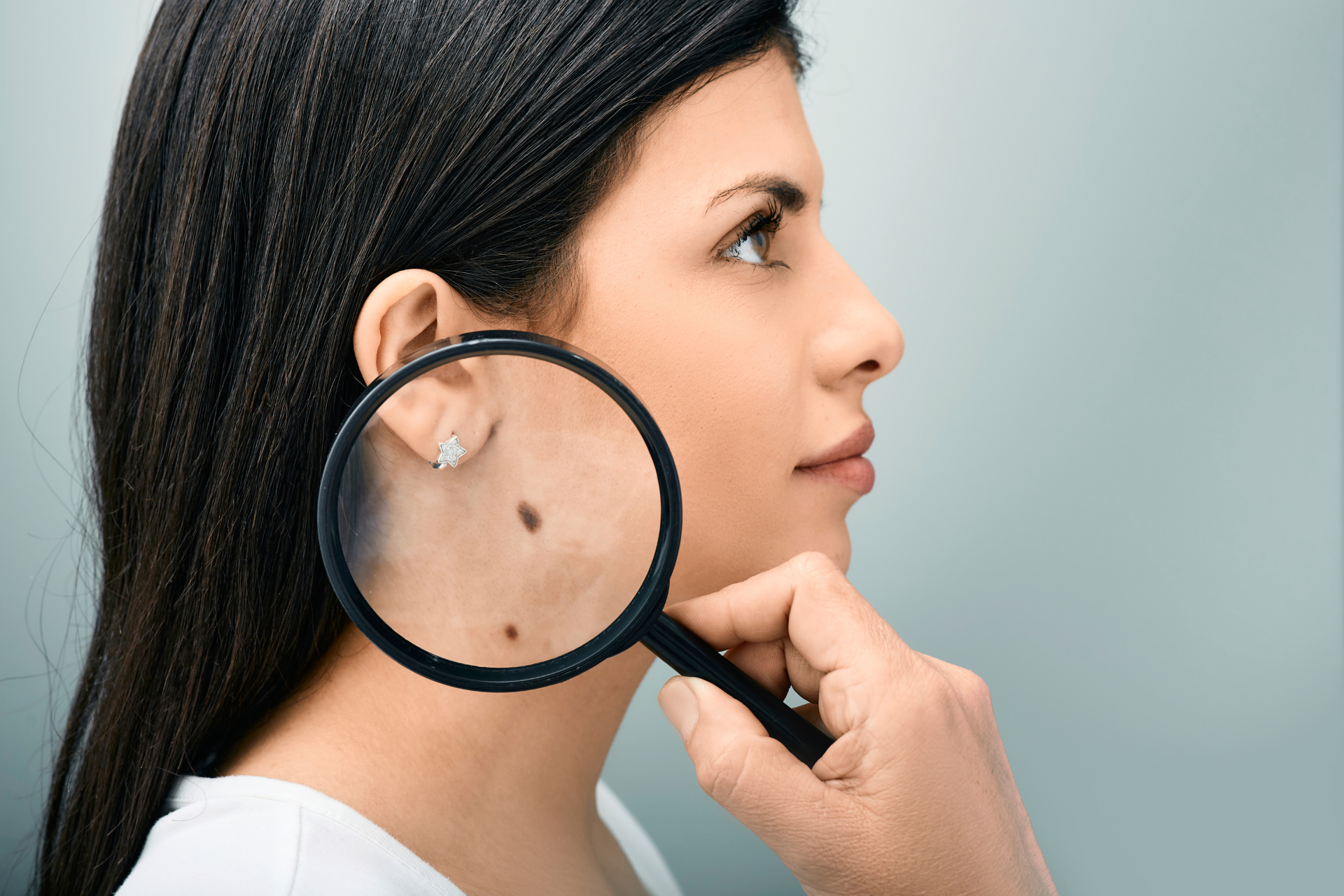
5 - Moles
Having numerous moles or dysplastic nevi (atypical moles) can elevate the risk of melanoma.
6 - Previous Skin Cancer
People who have previously been diagnosed with skin cancer are at a higher risk of developing it again.
Pathogenesis
1 - DNA Damage
- UV radiation can cause direct DNA damage or produce reactive oxygen species that damage DNA.
- When DNA is damaged, it can result in mutations, which may disable genes that typically regulate cell growth and division.
2 - Cell Mutation and Growth
- If the mutations occur in oncogenes (genes that stimulate cell division) or tumor suppressor genes (genes that inhibit cell division), it can lead to uncontrolled cell growth.
- The accumulation of mutations over time can cause cells to grow uncontrollably and form a mass or tumor.
3 - Invasion and Metastasis:
In the case of malignant melanoma, cancer cells can invade deeper into the skin and even spread to other parts of the body, a process known as metastasis.
Types of Skin Cancer
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
- Most common and least aggressive form of skin cancer.
- Originates in the basal cells, which produce new skin cells.
- Appears as a shiny, translucent, or pearly nodule.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
- Originates in the squamous cells, which form the surface of the skin.
- Can appear as a firm, red nodule or a flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface.
- More likely than BCC to spread to other parts of the body.
Melanoma
- Develops in melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin.
- Appears as a new spot or an existing mole that changes size, shape, or colour.
- Is highly aggressive and can spread to other parts of the body quickly.
Prevention is crucial when it comes to skin cancer. This includes limiting UV exposure, using sunscreen, sunglasses, wearing protective clothing, and conducting regular skin checks for any new or changing lesions. It's also vital to seek medical advice if any suspicious skin changes are noticed to ensure early detection and treatment, which significantly improves outcomes.
More Skin Tips.
CoreBodi