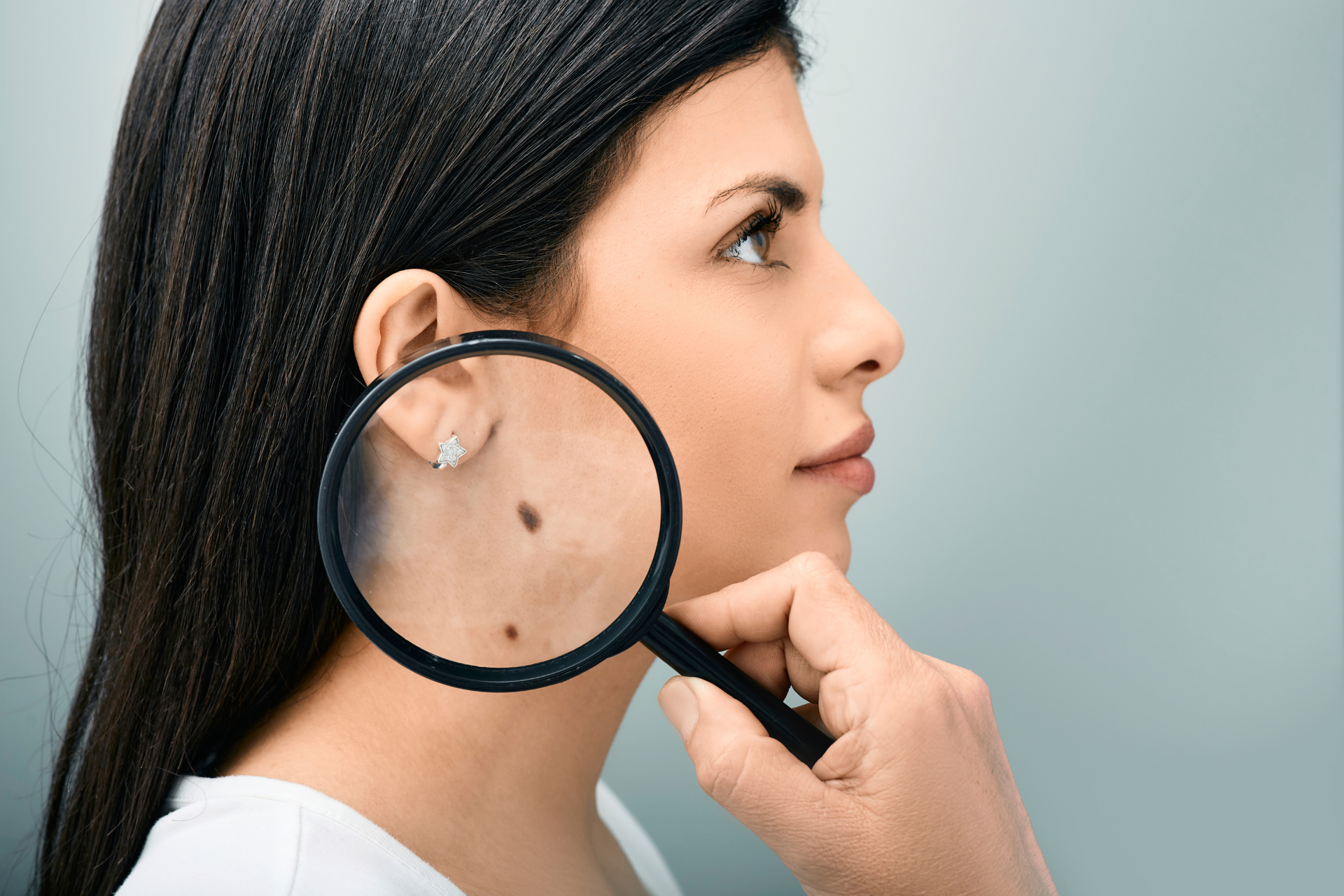
Skin Cancer and Aging: Protecting Your Skin as You Grow Older
Skin Cancer and Aging: Protecting Your Skin as You Grow Older

As we age, not only do we have to deal with wrinkles and grey hair, but our skin also becomes more susceptible to the harmful effects of the sun, increasing the risk of skin cancer.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of skin cancer in relation to aging.
We'll look at its types, prevention strategies, and treatments that are particularly relevant to older adults.
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer globally, and its incidence is on the rise.
A staggering one in five Australians will develop skin cancer by the age of 70.
Therefore, understanding this disease is crucial for your well-being.
Importance of Skin Care with Aging
Aging skin is not just an aesthetic concern; it also signals a weakening of the skin's protective functions.
This makes older adults more vulnerable to various skin issues, including cancer.
Let's have a look into why and how aging impacts skin health and ways to mitigate these risks.
Brief Overview of Skin Cancer
The Connection Between Aging and Skin Cancer
Aging and skin cancer are interconnected in more ways than you might think.
Let's dive into the science behind how aging affects the skin and how these changes increase your risk of developing skin cancer.
How Aging Affects Skin Health
As we age, our skin naturally loses elasticity, moisture, and its ability to repair itself.
Collagen production declines, making the skin thinner and less resilient. Furthermore, the skin's natural ability to protect itself from harmful UV rays diminishes. Consequently, the older you get, the more prone you are to the negative impacts of sun exposure, including skin cancer.
Specific Risks for Older Adults
Older adults face unique challenges when it comes to skin health.
First off, they usually have a longer history of sun exposure, which raises their risk of developing skin issues.
Also, the body's ability to repair DNA damage decreases with age, making it more difficult to recover from sunburn or to control abnormal cell growth, which could lead to cancer.
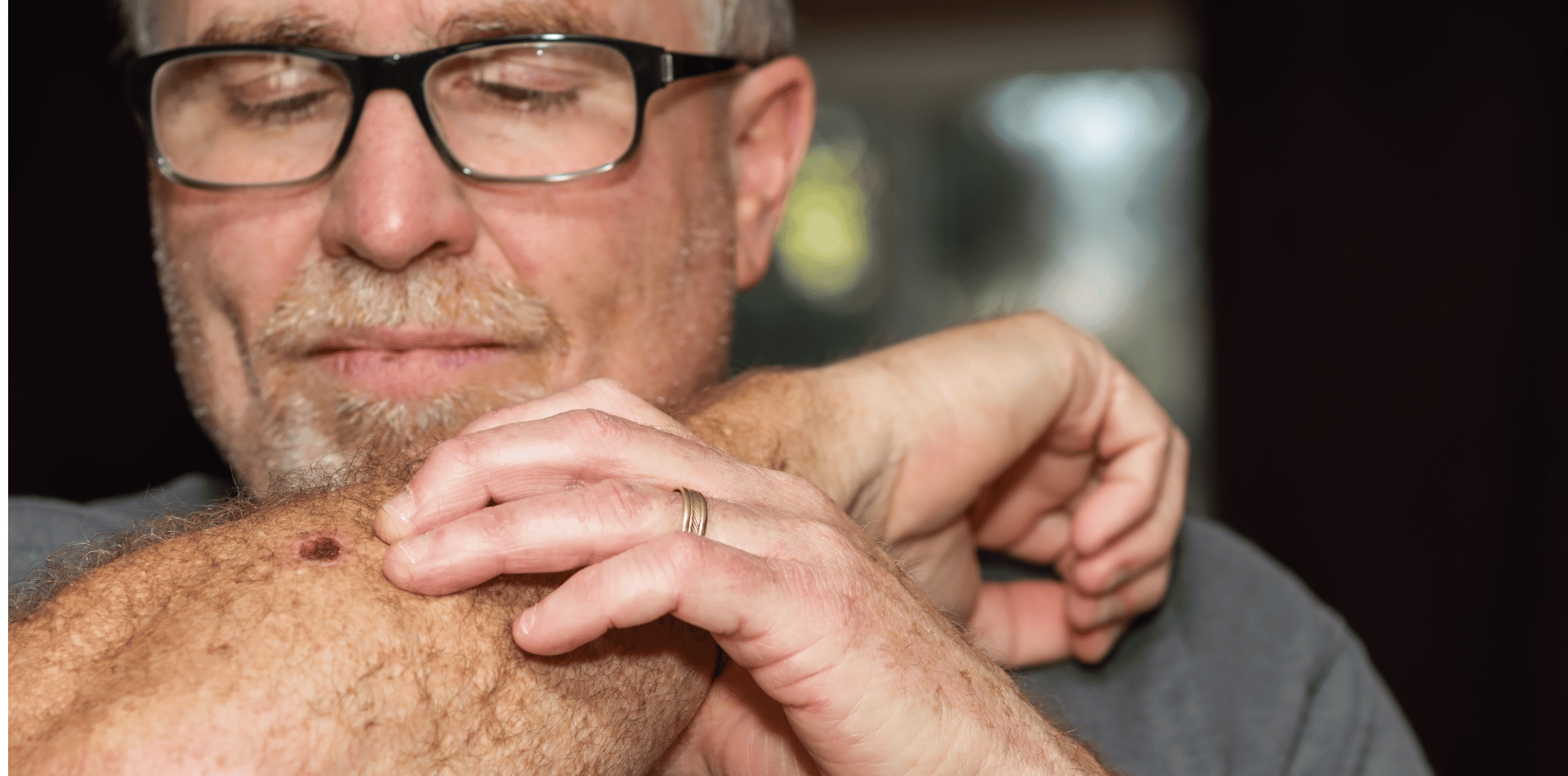
Types of Skin Cancer Older Adults Should Be Aware Of
While skin cancer can come in various forms, there are three primary types that older adults should be particularly aware of.
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common type of skin cancer. It often appears as a raised, smooth bump on sun-exposed skin, such as the face, ears, and neck. Fortunately, basal cell carcinoma is usually slow-growing and rarely metastasises, meaning it seldom spreads to other parts of the body.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma typically manifests as a red, scaly patch or as a lump that seems to grow rapidly. This type is more aggressive than basal cell carcinoma and has a higher risk of spreading if not treated promptly.
Melanoma
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer.
It often appears as a new or changing mole.
Unlike the other types, melanoma can spread quickly to other parts of the body, making early detection and treatment vital.
Prevention Strategies: What You Can Do Now
The good news is that there are several steps you can take to protect your aging skin from the harmful effects of the sun and decrease your risk of developing skin cancer.
Daily Sunscreen Use
Wearing sunscreen daily is your first line of defense against harmful UV rays.
Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 50 and apply it generously to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days and during the winter.
Wearing Protective Clothing
Clothing can act as a physical barrier between the sun's rays and your skin.
Opt for long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses with UV protection to maximize your defense against the sun.
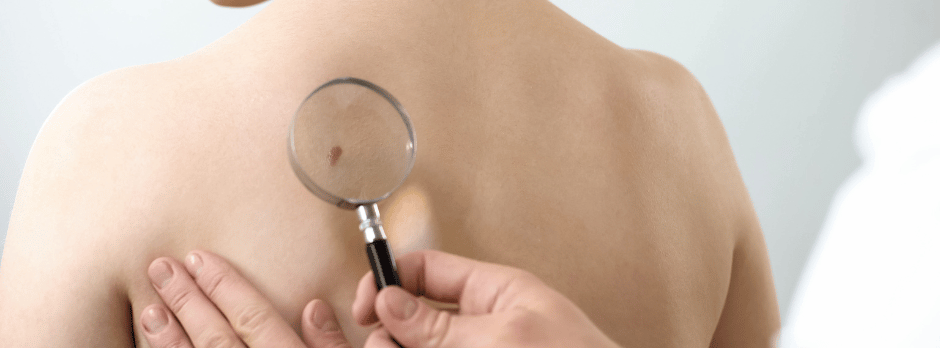
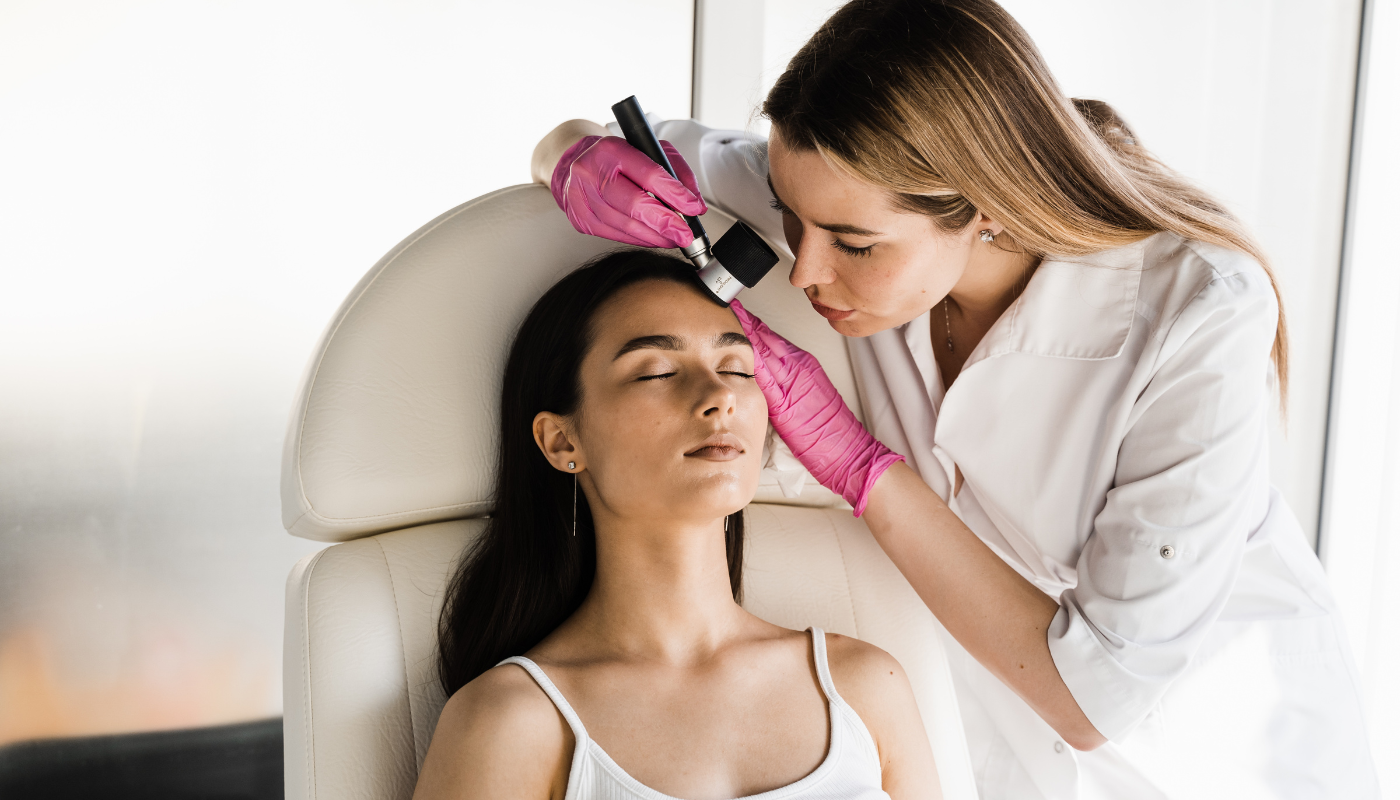
Regular Skin Checks
Early detection plays a crucial role in effectively treating skin cancer.
Therefore, make a habit of checking your skin at least once a month. Look for new or changing moles, lumps, or patches of discoloured skin.
Additionally, schedule annual appointments with a dermatologist for a professional skin examination.
Treatment Options for Older Adults
If you are diagnosed with skin cancer, various treatment options are available, tailored to your age, health, and the type of skin cancer.
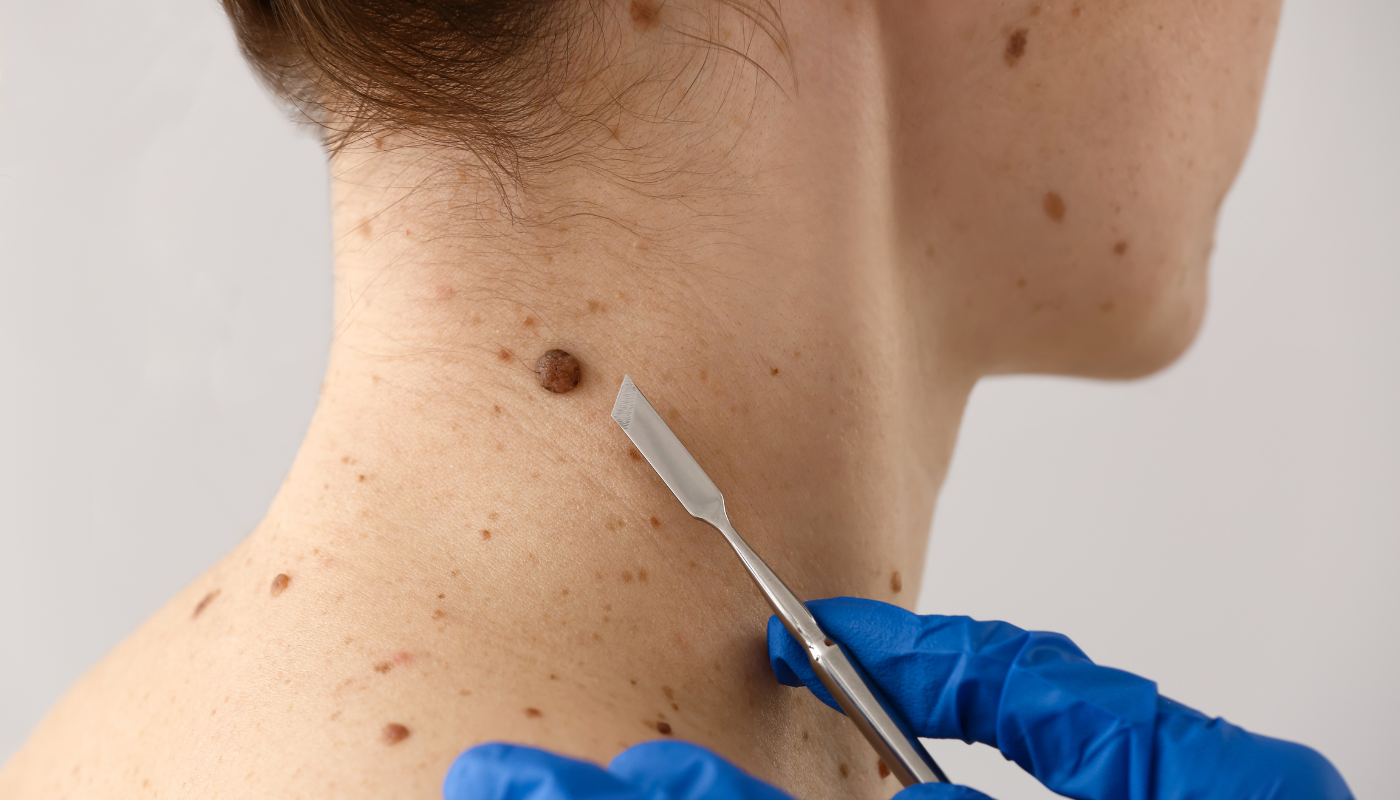
Surgical Removal
The most common and effective treatment for skin cancers like basal and squamous cell carcinoma is surgical removal.
The procedure involves excising the cancerous tissue and some surrounding healthy tissue to ensure complete removal.
Radiation and Chemotherapy
For more advanced or aggressive cancers, radiation or chemotherapy may be recommended.
These treatments aim to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing but can come with a host of side effects.
Newer Treatments: Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy
Recent advancements in cancer treatment have introduced options like immunotherapy and targeted therapy, which can be less invasive and more effective in certain cases. These treatments work by harnessing the body’s immune system or targeting specific genetic mutations in cancer cells.
A Healthy Future: Protecting Your Aging Skin
Protecting your skin from the harmful effects of the sun is essential at any age, but it becomes even more critical as we grow older due to increased susceptibility to skin cancer.
Recap of Prevention Strategies
Remember, prevention is always better than cure.
Using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and performing regular skin checks are simple yet effective ways to safeguard your skin.
Final Thoughts
Aging is a natural part of life, but that doesn't mean you have to accept the increased risk of skin cancer as an inevitable part of growing older. With the right knowledge and prevention strategies, you can take active steps to maintain your skin health as you age.
FAQ
We understand you may have specific questions about skin cancer and aging, so we've compiled a list of frequently asked questions to address those concerns.
What age should I start worrying about skin cancer?
While the risk increases with age, skin cancer can develop at any age. However, people over 50 are advised to be more vigilant.
Is skin cancer hereditary?
Certain types of skin cancer have genetic factors, but sun exposure is the most significant risk factor for most people.
Can I stop using sunscreen in winter?
No, UV rays can still be harmful in winter, especially if you're in snow-covered areas where the rays can reflect off the surface.
By educating yourself and taking precautionary measures, you can protect your skin from the damaging effects of the sun and reduce your risk of developing skin cancer, no matter your age.
More Skin Tips.
CoreBodi