Knowledge is Power: Understanding and Preventing Skin Cancer
Understanding and Preventing Skin Cancer!

Skin cancer is one of the most common yet preventable forms of cancer.
While it can affect anyone, certain risk factors make some individuals more susceptible than others.
Understanding these risks and adopting proactive measures can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing this potentially life-threatening disease.
The Role of Knowledge in Skin Cancer Prevention
The first step in preventing skin cancer is awareness.
By recognizing the factors that contribute to its development, individuals can take meaningful steps to protect themselves. The key lies in minimizing exposure to harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, making informed choices about sun safety, and seeking medical attention for any suspicious skin changes.
Common Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
1. Excessive Sun Exposure
One of the most significant contributors to skin cancer is prolonged and unprotected exposure to the sun’s UV rays.
The sun emits two types of harmful UV radiation: UVA and UVB.
- UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin and contribute to premature aging and long-term damage.
- UVB rays primarily cause sunburns and direct DNA damage, leading to skin cancer over time.
Spending long hours in direct sunlight, particularly between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. when UV radiation is at its peak, significantly increases the risk. Outdoor workers, athletes, and those who frequently engage in sunbathing are at higher risk of overexposure.
Prevention Tips:
- Limit direct sun exposure, especially during peak hours.
- Always seek shade when outdoors.
- Wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses with UV protection.
- Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30 or higher) daily, even on cloudy days.
2. Fair Skin & Light Features
People with fair skin, light-coloured eyes, and blonde or red hair have lower levels of melanin, the pigment that provides some natural protection against UV radiation.
As a result, they are more prone to sunburns and cellular damage that can lead to skin cancer.
While people with darker skin have higher melanin levels, they are not immune to skin cancer and should also take preventive measures.
Prevention Tips:
- Fair-skinned individuals should be extra vigilant about sun protection.
- Regular use of high-SPF (50) sunscreen is essential.
- Annual dermatological skin checks can help catch any abnormalities early.
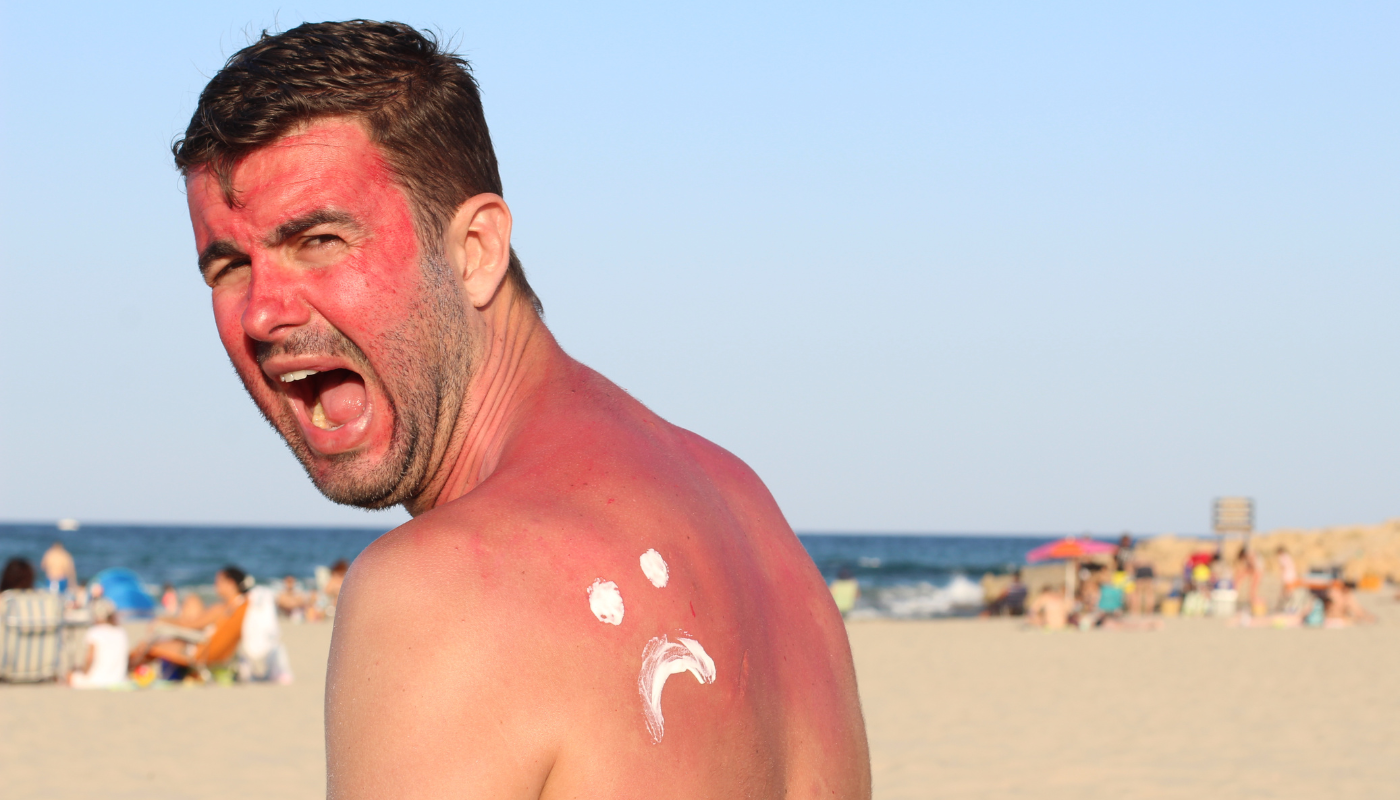
3. History of Sunburns
Severe sunburns, particularly those experienced during childhood and adolescence, increase the risk of developing skin cancer later in life.
Blistering sunburns indicate significant skin damage, which can lead to DNA mutations that trigger abnormal cell growth.
Prevention Tips:
- Avoid sunburns by wearing protective clothing and using sunscreen.
- Teach children proper sun safety to reduce their risk in adulthood.
- Treat sunburns promptly with cool compresses and aloe vera to soothe damaged skin.

4. Family History of Skin Cancer
Genetics play a role in an individual’s susceptibility to skin cancer.
If a close family member has been diagnosed with melanoma or other forms of skin cancer, your risk may be higher.
This is due to inherited genetic mutations that make some people more prone to cellular abnormalities.
Prevention Tips:
- Know your family history and discuss it with your doctor.
- Undergo regular skin screenings if you have a genetic predisposition.
- Be vigilant about checking your skin for new or changing moles.
5. Frequent Tanning
Tanning, whether from natural sunlight or indoor tanning beds, significantly increases the risk of skin cancer.
Tanning beds emit concentrated UV radiation that penetrates deep into the skin, accelerating skin aging and increasing the likelihood of cancerous mutations.
Prevention Tips:
- Avoid tanning beds entirely.
- Opt for sunless tanning lotions or sprays if you desire a tanned appearance.
- Educate young adults about the dangers of tanning and encourage healthier alternatives.
Taking Action: How to Protect Your Skin
Beyond understanding risk factors, taking practical steps to protect your skin is crucial.
Incorporating daily sun protection into your routine and being proactive about skin health can go a long way in preventing skin cancer
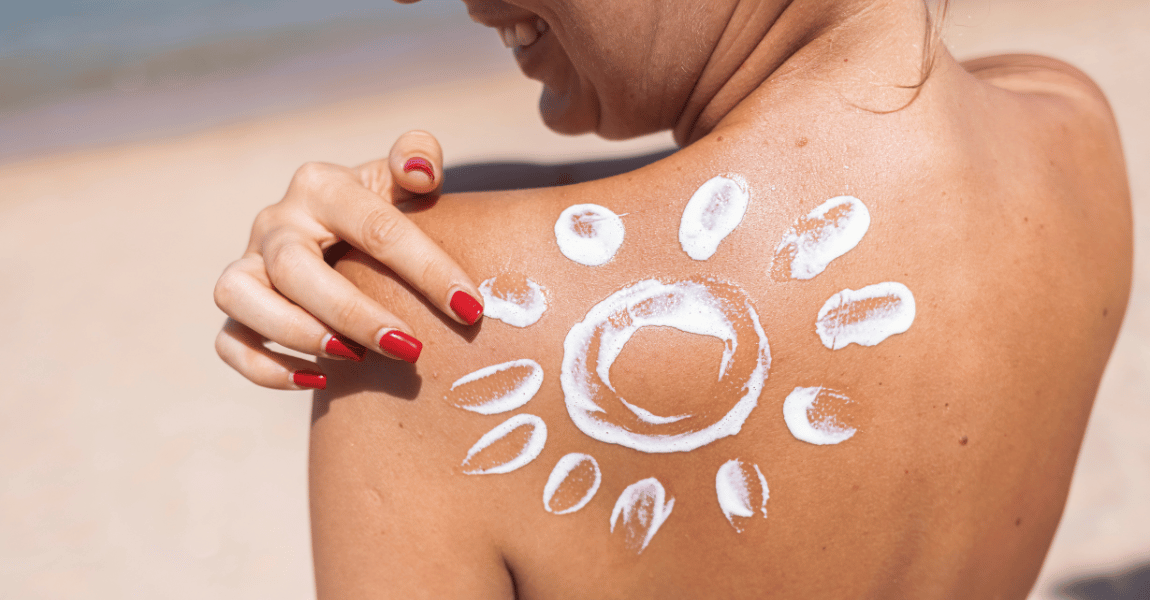
1. Use Sunscreen Daily
Sunscreen is a powerful tool against UV radiation.
Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher and apply it generously to all exposed areas of skin.
Reapply every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating.
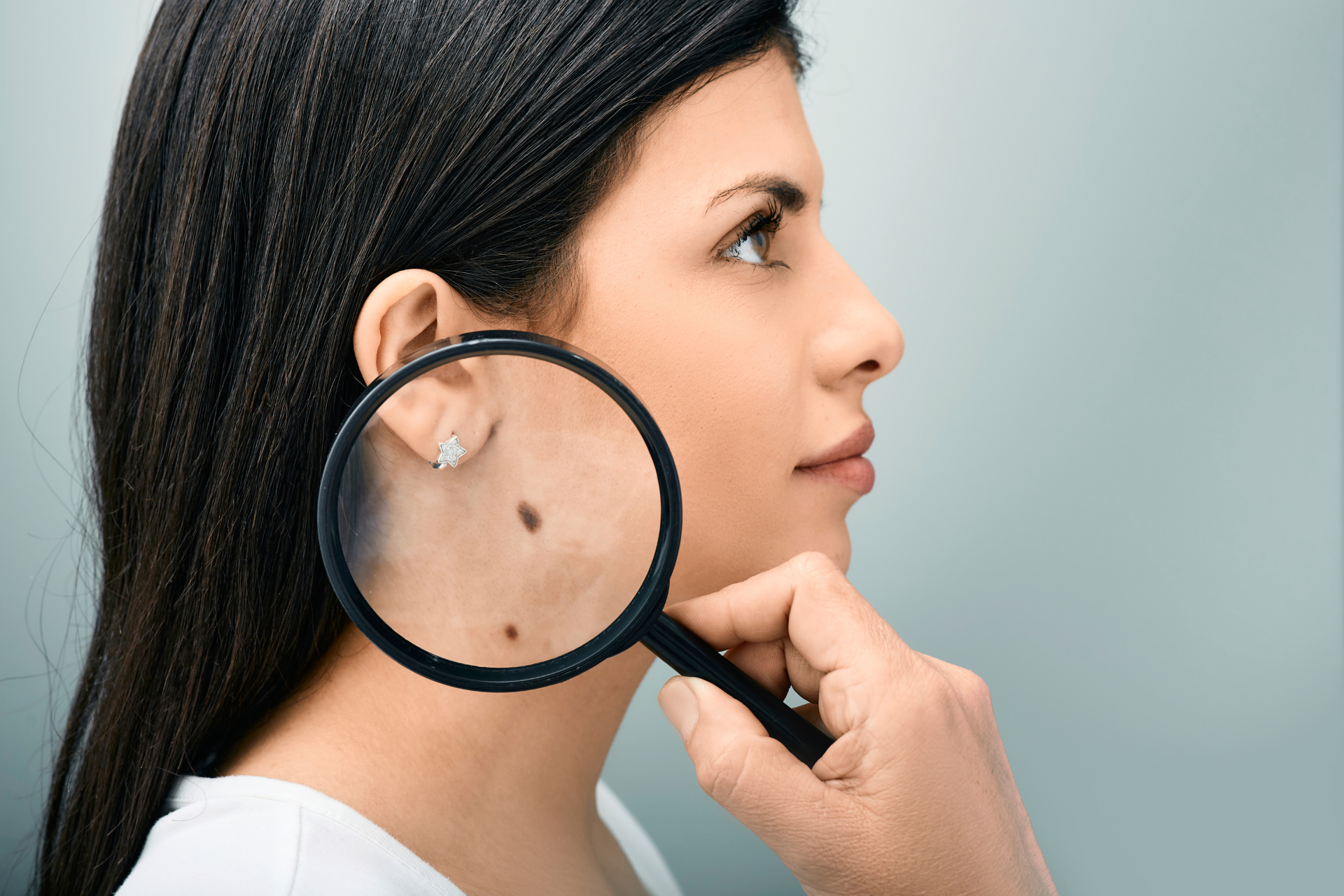
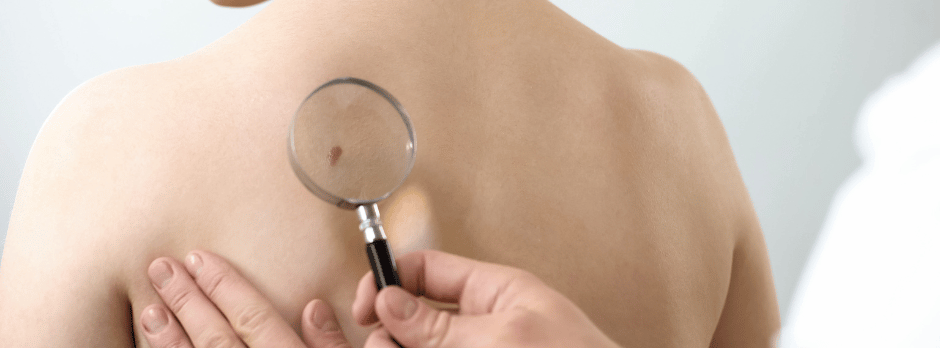
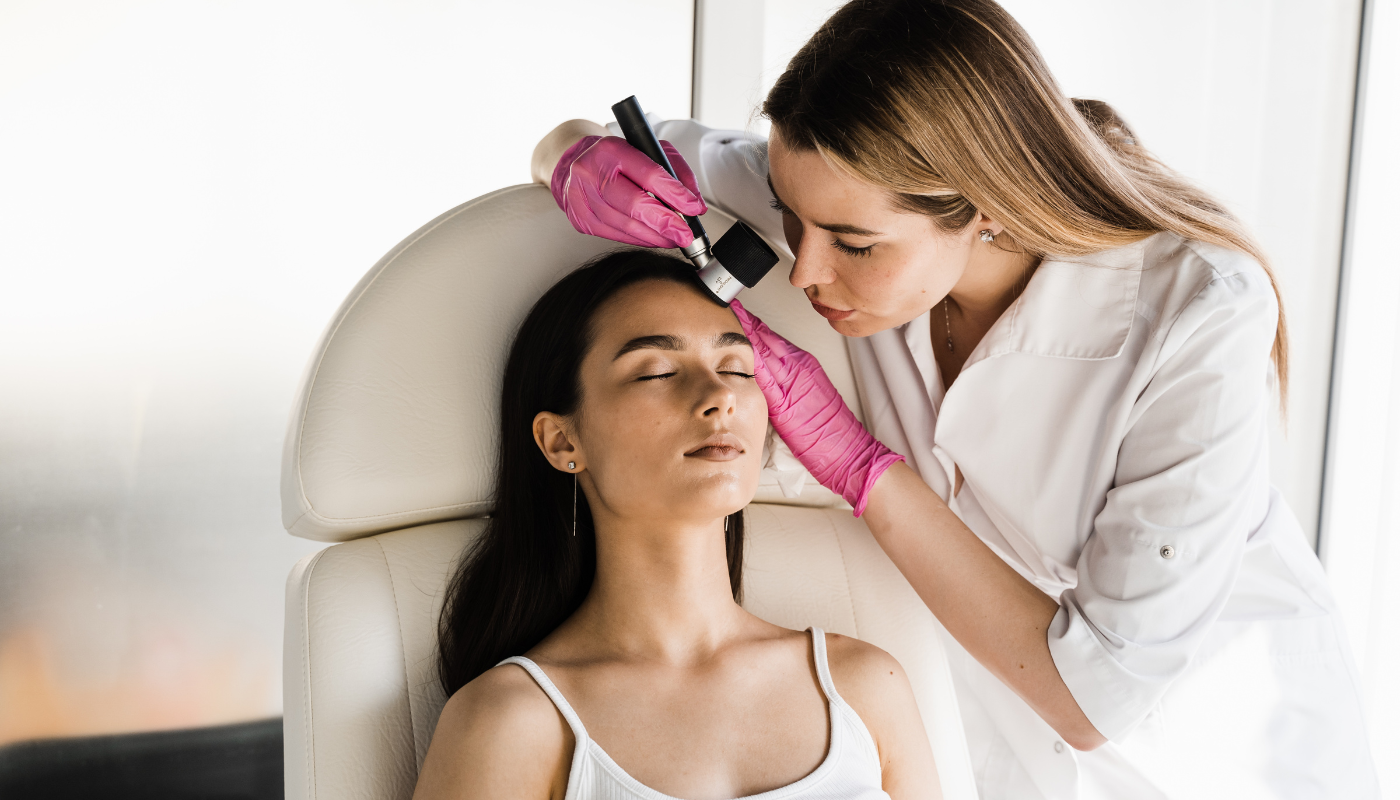
2. Perform Regular Skin Checks
Self-examinations can help detect skin cancer early.
Use the ABCDE rule to assess moles and skin lesions:
- A – Asymmetry: One half of the mole does not match the other.
- B – Border: Irregular, blurred, or jagged edges.
- C – Colour: Multiple colours or unusual shades (red, blue, white, or black).
- D – Diameter: Larger than a pencil eraser (6mm).
- E – Evolving: Changes in size, shape, or color over time.
If you notice any of these warning signs, consult a dermatologist immediately.
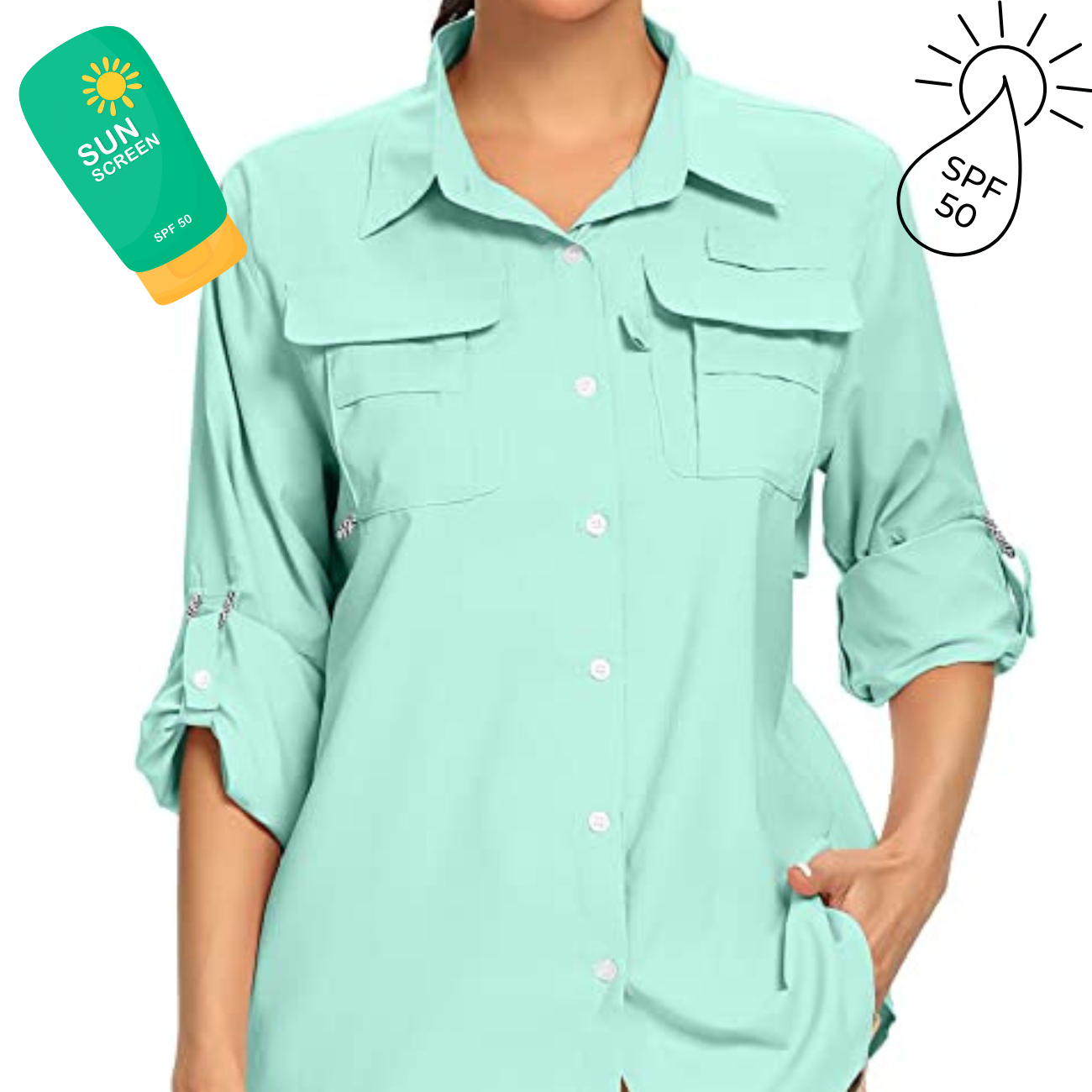

3. Wear Protective Clothing
Clothing is an effective barrier against UV rays. Opt for tightly woven fabrics and UV-protective clothing.
A wide-brimmed hat and UV-blocking sunglasses can further shield your skin from sun damage.
4. Avoid Peak Sun Hours
Whenever possible, plan outdoor activities in the early morning or late afternoon to minimize UV exposure.
If you must be outside during peak hours, seek shade or use an umbrella.
5. Maintain a Healthy Diet
A diet rich in antioxidants can help protect skin cells from damage.
Foods high in vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and omega-3 fatty acids support skin health and may reduce the risk of skin cancer.
The Bottom Line: Prevention is Key
While skin cancer is common, it is also one of the most preventable forms of cancer.
Knowledge truly is power when it comes to protecting yourself and your loved ones.
By understanding the risk factors and taking proactive measures, you can significantly reduce your chances of developing skin cancer.
Sun safety should be a lifelong commitment, starting in childhood and continuing through adulthood. Regular skin checks, sunscreen use, and avoidance of harmful UV exposure can help keep your skin healthy and cancer-free.
If you have concerns about your skin or notice any unusual changes, don’t wait—seek medical advice as soon as possible.
Early detection and prevention can save lives.
More Skin Tips.
CoreBodi